ความจำใช้งานคืออะไร? ทำแบบประเมินความรู้ความเข้าใจออนไลน์ฟรีเพื่อพัฒนาความจำใช้งานของคุณ
December 15, 2025 | By Gideon Albright
คุณเคยเดินเข้าไปในห้องแล้วลืมไปเลยว่าเข้ามาทำไมหรือไม่? หรือคุณเคยประสบปัญหาในการทำตามสูตรอาหารที่ซับซ้อนซึ่งมีหลายขั้นตอนหรือไม่? ประสบการณ์ทั่วไปเหล่านี้เชื่อมโยงโดยตรงกับเครื่องมือทางจิตอันทรงพลังที่เรียกว่า ความจำใช้งาน (working memory) มันคือกลไกที่ขับเคลื่อนการคิด การแก้ปัญหา และการเรียนรู้ประจำวันของเราเป็นส่วนใหญ่
แต่ความจำใช้งานคืออะไรกันแน่ และคุณสามารถทำอะไรเพื่อทำให้มันแข็งแกร่งขึ้นได้หรือไม่? คู่มือนี้จะสำรวจทักษะทางความรู้ความเข้าใจที่สำคัญนี้ในแง่ง่ายๆ เราจะกล่าวถึงความแตกต่างจากความจำระยะสั้น เหตุใดจึงจำเป็นต่อความสำเร็จ และจะประเมินได้อย่างไร ที่สำคัญที่สุด คุณจะได้เรียนรู้กลยุทธ์ที่นำไปใช้ได้จริงและได้รับการสนับสนุนจากวิทยาศาสตร์เพื่อเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพของมัน
ต้องการปลดล็อกศักยภาพสูงสุดของคุณใช่หรือไม่? เริ่มต้นด้วยการทำความเข้าใจโปรไฟล์ความรู้ความเข้าใจของคุณ การประเมินความรู้ความเข้าใจออนไลน์ที่ครอบคลุม จะให้ข้อมูลพื้นฐานที่ชัดเจนเกี่ยวกับความจำใช้งานของคุณและอื่นๆ อีกมากมาย ซึ่งจะให้ข้อมูลเชิงลึกเฉพาะบุคคลสำหรับการเดินทางของคุณ

ความจำใช้งานคืออะไรกันแน่?
ลองนึกภาพ ความจำใช้งาน ของคุณว่าเป็นพื้นที่ทำงานทางจิตของสมอง หรือกระดาษโน้ตชั่วคราว เป็นระบบที่ช่วยให้คุณเก็บข้อมูลจำนวนเล็กน้อยไว้ในใจได้ช่วงเวลาสั้นๆ และ ประมวลผลกับมัน ไม่ใช่แค่การจัดเก็บข้อมูลเท่านั้น แต่ยังเกี่ยวกับการจัดเก็บและจัดการข้อมูลไปพร้อมๆ กันเพื่อทำงานให้สำเร็จ
ตัวอย่างเช่น เมื่อคุณคำนวณทิป 15% จากบิลร้านอาหารในหัว คุณกำลังใช้ ความจำใช้งาน คุณต้องจำยอดบิลเดิม คำนวณ 10% จากนั้น 5% และสุดท้ายก็บวกทั้งหมดเข้าด้วยกัน กระบวนการเชิงรุก ในการเก็บ ประมวลผล และรวมข้อมูลนี้เป็นหน้าที่หลักของ ความจำใช้งาน
ความแตกต่างระหว่างความจำใช้งานและความจำระยะสั้น
ผู้คนมักใช้คำว่า "ความจำใช้งาน" และ "ความจำระยะสั้น" สลับกันไปมา แต่จริงๆ แล้วมันไม่เหมือนกัน การเข้าใจความแตกต่างเป็นสิ่งสำคัญในการทำความเข้าใจว่าสมองของคุณทำงานอย่างไร
- ความจำระยะสั้น เป็นระบบจัดเก็บข้อมูลแบบพาสซีฟ เปรียบเสมือนพื้นที่พักข้อมูลชั่วคราวสำหรับข้อมูลล่าสุด เช่น การจำหมายเลขโทรศัพท์ได้นานพอที่จะจดลงไป มันเก็บข้อมูลโดยไม่ได้ทำอะไรกับมัน
- ความจำใช้งาน เป็น ระบบเชิงรุก มันเกี่ยวข้องกับการเก็บข้อมูลและประมวลผลหรือจัดการข้อมูลอย่าง เชิงรุก นั่นคือส่วนที่เป็น "งาน" ที่ทำให้มันแตกต่าง ตัวอย่างเช่น หากคุณต้องพูดหมายเลขโทรศัพท์เดียวกันนั้นย้อนกลับ คุณกำลังใช้ ความจำใช้งาน ของคุณ
สรุปง่ายๆ: ความจำระยะสั้นแค่เก็บข้อมูล ความจำใช้งานนำข้อมูลไปใช้งาน
เหตุใดความจำใช้งานจึงสำคัญต่อชีวิตประจำวันและการเรียนรู้
ความจำใช้งาน ที่แข็งแกร่งคือพลังวิเศษในโลกที่เต็มไปด้วยข้อมูลในปัจจุบัน เป็นพื้นฐานสำหรับงานทางความรู้ความเข้าใจที่ซับซ้อนเกือบทุกอย่างที่เราทำ ความสามารถของมันส่งผลโดยตรงต่อความสามารถในการเรียนรู้ การให้เหตุผล และการรับมือกับความท้าทายในชีวิตประจำวันของเรา
นี่คือบางส่วนที่มันมีบทบาทสำคัญ:
- การเรียนรู้: การติดตามการบรรยายของครู การจดบันทึก และการเชื่อมโยงแนวคิดใหม่ๆ กับสิ่งที่คุณรู้แล้ว ล้วนอาศัย ความจำใช้งาน
- ความเข้าใจในการอ่าน: ในการทำความเข้าใจย่อหน้า คุณต้องเก็บจุดเริ่มต้นของประโยคไว้ในใจขณะที่คุณอ่านไปจนจบ
- การแก้ปัญหา: การติดตามข้อมูลต่างๆ เป็นสิ่งสำคัญสำหรับการวางแผน การวางกลยุทธ์ และการหาทางออก
- การปฏิบัติตามคำสั่ง: ไม่ว่าจะเป็นการประกอบเฟอร์นิเจอร์หรือการทำตามสูตรอาหารใหม่ คุณต้องจำแต่ละขั้นตอนและลำดับของมัน
- การสนทนา: ช่วยให้คุณจำสิ่งที่อีกฝ่ายพูดได้ในขณะที่คุณกำลังคิดคำตอบ
ประเมินความจำใช้งานอย่างไร? การทดสอบและวิธีการที่สำคัญ
เนื่องจาก ความจำใช้งาน มีความสำคัญมาก นักจิตวิทยาและนักประสาทวิทยาจึงได้พัฒนาวิธีการต่างๆ ในการวัดผล การประเมินทักษะทางความรู้ความเข้าใจช่วยระบุความสามารถของแต่ละบุคคลในการเก็บและจัดการข้อมูล สิ่งนี้เผยให้เห็นจุดแข็งทางความรู้ความเข้าใจและพื้นที่ที่อาจต้องปรับปรุง
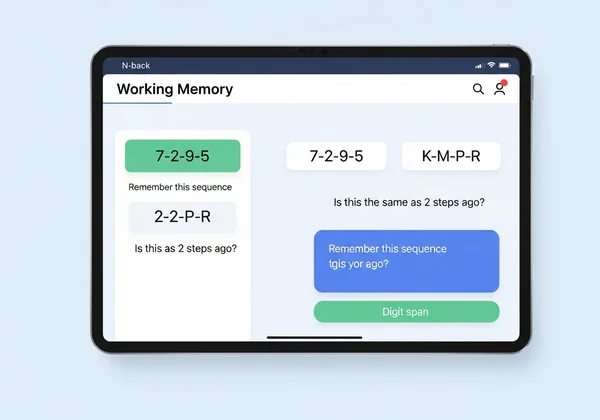
การทดสอบความจำใช้งานแบบดั้งเดิม: ตั้งแต่ Digit Span ไปจนถึง N-Back
เป็นเวลาหลายทศวรรษที่การประเมินความรู้ความเข้าใจได้ใช้ภารกิจเฉพาะเพื่อประเมิน ความจำใช้งาน คุณอาจเคยได้ยินบางส่วนของพวกมันด้วยซ้ำ
- การทดสอบ Digit Span: นี่คือการทดสอบแบบคลาสสิกที่บุคคลจะได้รับคำขอให้ฟังลำดับตัวเลขแล้วพูดซ้ำ ในเวอร์ชันที่ซับซ้อนกว่า พวกเขาต้องพูดตัวเลขย้อนกลับ ซึ่งจะใช้ส่วน "ใช้งาน" อย่างมาก
- N-Back Task: ในภารกิจนี้ ผู้เข้าร่วมจะถูกแสดงลำดับของรายการ (เช่น ตัวอักษรหรือรูปภาพ) ทีละรายการ พวกเขาต้องระบุว่ารายการปัจจุบันเหมือนกับรายการที่แสดง 'n' ขั้นตอนก่อนหน้าหรือไม่ (เช่น 2 ขั้นตอนก่อนหน้า) ซึ่งต้องมีการอัปเดตข้อมูลที่เก็บไว้ในพื้นที่ทำงานทางจิตอย่างต่อเนื่อง
วิธีการแบบดั้งเดิมเหล่านี้มีคุณค่า แต่บ่อยครั้งต้องใช้การตั้งค่าทางคลินิกและผู้ดูแลที่ได้รับการฝึกฝน
บทบาทของการประเมินความรู้ความเข้าใจออนไลน์ในการประเมินความจำใช้งาน
ปัจจุบัน เทคโนโลยีทำให้การประเมินความรู้ความเข้าใจเข้าถึงได้ง่ายกว่าที่เคยเป็นมา แพลตฟอร์มออนไลน์สมัยใหม่นำเสนอวิธีที่สะดวกและมีประสิทธิภาพในการประเมิน ความจำใช้งาน และทักษะทางความรู้ความเข้าใจอื่นๆ จากความสะดวกสบายในบ้านของคุณ
แพลตฟอร์มขั้นสูงเช่น เครื่องมือที่ขับเคลื่อนด้วย AI ของเรา ก้าวไปไกลกว่าคะแนนพื้นฐาน พวกเขาใช้ AI เพื่อวิเคราะห์รูปแบบการตอบสนอง เวลา และความถูกต้องของคุณ ผลลัพธ์? รายงานโดยละเอียดและเป็นส่วนตัวที่ให้ความเข้าใจอย่างลึกซึ้งยิ่งขึ้นเกี่ยวกับโปรไฟล์ความรู้ความเข้าใจของคุณ สิ่งนี้ไม่ได้ให้แค่ข้อมูลเท่านั้น แต่ยังให้ข้อมูลเชิงลึกที่นำไปใช้ได้จริงว่าจิตใจของคุณทำงานอย่างไร
ความท้าทายและการลดลงของความจำใช้งานที่พบบ่อยในทุกวัย
เป็นเรื่องปกติที่ความสามารถของ ความจำใช้งาน จะผันผวน ปัจจัยต่างๆ เช่น ความเครียดหรือความเหนื่อยล้าอาจทำให้ประสิทธิภาพลดลงชั่วคราว อย่างไรก็ตาม บางคนอาจประสบปัญหาที่คงอยู่นานกว่าซึ่งส่งผลกระทบต่อชีวิตประจำวันของพวกเขา
การจดจำสัญญาณของการบกพร่องของความจำใช้งาน
หากคุณหรือคนที่คุณรู้จักกำลังประสบปัญหาเกี่ยวกับ ความจำใช้งาน คุณอาจสังเกตเห็นสัญญาณบางอย่างที่พบบ่อย สิ่งสำคัญคือต้องจำไว้ว่าการประสบสิ่งเหล่านี้เป็นครั้งคราวเป็นเรื่องปกติ แต่รูปแบบที่สม่ำเสมออาจคุ้มค่าที่จะสำรวจเพิ่มเติม
สัญญาณที่พบบ่อย ได้แก่:
- มีปัญหาในการติดตามการสนทนาหรือคำแนะนำหลายขั้นตอน
- หลุดประเด็นความคิดบ่อยๆ กลางประโยค
- มีปัญหาในการคำนวณเลขในใจที่เคยทำได้ง่าย
- ลืมจุดประสงค์ของการกระทำ เช่น ทำไมคุณถึงเข้ามาในห้อง
- พบว่าเป็นการยากที่จะจัดระเบียบและทำโครงการที่ซับซ้อนให้สำเร็จ
ปัจจัยที่สามารถส่งผลกระทบต่อประสิทธิภาพของความจำใช้งาน
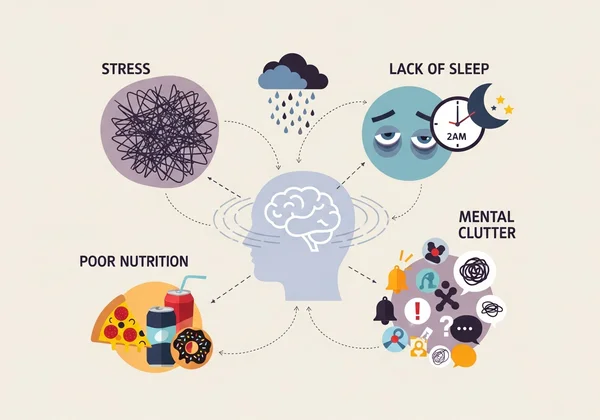
ปัจจัยหลายอย่างสามารถส่งผลต่อการทำงานของ ความจำใช้งาน ของคุณ ยิ่งไปกว่านั้น คุณสามารถจัดการกับส่วนใหญ่ได้ด้วยตัวเอง
-
ความเครียดและความวิตกกังวล: ระดับคอร์ติซอล (ฮอร์โมนความเครียด) ที่สูงสามารถรบกวน prefrontal cortex ซึ่งเป็นบริเวณสมองที่สำคัญสำหรับความจำใช้งาน
-
การนอนหลับไม่เพียงพอ: การนอนหลับเป็นสิ่งสำคัญสำหรับการรวมความจำและการฟื้นฟูสมอง การนอนหลับที่ไม่ดีอย่างต่อเนื่องนำไปสู่ประสิทธิภาพการรับรู้ที่แย่ลง
-
โภชนาการที่ไม่ดี: สมองของคุณต้องการเชื้อเพลิงที่เหมาะสม อาหารที่ขาดสารอาหารที่จำเป็น เช่น กรดไขมันโอเมก้า 3 และสารต้านอนุมูลอิสระสามารถบั่นทอนการทำงานของการรับรู้
-
การขาดการกระตุ้นทางจิตใจ: เช่นเดียวกับกล้ามเนื้อ สมองได้รับประโยชน์จากการออกกำลังกายอย่างสม่ำเสมอ การขาดกิจกรรมที่น่าสนใจอาจนำไปสู่การลดลงของการทำงาน
-
ความชรา: แม้ว่าการลดลงที่เกี่ยวข้องกับอายุบางอย่างจะเป็นเรื่องปกติ แต่การใช้ชีวิตที่ กระฉับกระเฉง และมีสุขภาพดีสามารถบรรเทาผลกระทบได้อย่างมีนัยสำคัญ
กลยุทธ์ที่ได้รับการสนับสนุนจากวิทยาศาสตร์เพื่อปรับปรุงความจำใช้งานสำหรับผู้ใหญ่
สมองมีความสามารถที่น่าทึ่งในการปรับตัวและเปลี่ยนแปลง ซึ่งเป็นคุณสมบัติที่เรียกว่า neuroplasticity (ความยืดหยุ่นของสมอง) ซึ่งหมายความว่าด้วยกลยุทธ์ที่เหมาะสม คุณสามารถ ปรับปรุงประสิทธิภาพความจำใช้งาน ได้ทุกวัย ไม่ใช่เรื่องของการเปลี่ยนฮาร์ดแวร์ของสมอง แต่เป็นการฝึกฝนให้มันทำงานได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพมากขึ้น
การฝึกสมองและเกมฝึกสมอง
การฝึกสมองแบบกำหนดเป้าหมายสามารถเสริมสร้าง ความจำใช้งาน ของคุณได้ เกมฝึกสมองที่ท้าทายให้คุณเก็บและจัดการข้อมูลมีประสิทธิภาพเป็นพิเศษ มองหากิจกรรมที่ต้องใช้คุณ:
- จำลำดับ (เช่น ในเกม Simon)
- ไขปริศนาที่ซับซ้อนหรือเกมวางแผน (เช่น Sudoku หรือหมากรุก)
- ใช้แอปฝึก N-back ซึ่งออกแบบมาโดยเฉพาะเพื่อกำหนดเป้าหมาย ความจำใช้งาน
หัวใจสำคัญคือการหากิจกรรมที่ท้าทายแต่ไม่มากเกินไป ความสม่ำเสมอสำคัญกว่าความเข้มข้น
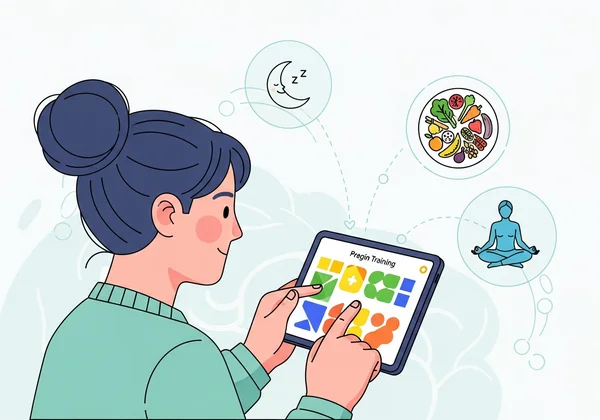
การปรับเปลี่ยนไลฟ์สไตล์: การนอนหลับ โภชนาการ และการมีสติ
พฤติกรรมประจำวันของคุณมีผลกระทบอย่างมากต่อสุขภาพสมองของคุณ การเปลี่ยนแปลงเล็กน้อยและสม่ำเสมอในสามด้านนี้สามารถนำไปสู่การปรับปรุง ความจำใช้งาน อย่างมีนัยสำคัญ
- จัดลำดับความสำคัญของการนอนหลับ: ตั้งเป้าหมายการนอนหลับที่มีคุณภาพ 7-9 ชั่วโมงต่อคืน กำหนดตารางการนอนหลับที่สม่ำเสมอและสร้างกิจวัตรการเข้านอนที่ผ่อนคลายเพื่อช่วยให้สมองของคุณชาร์จพลัง
- กินเพื่อสมองของคุณ: รวมอาหารบำรุงสมองเข้ากับอาหารของคุณ ซึ่งรวมถึงปลาที่มีไขมัน (อุดมไปด้วยโอเมก้า 3) บลูเบอร์รี่ (สารต้านอนุมูลอิสระ) ถั่ว และผักใบเขียว
- ฝึกสติ (Mindfulness): การทำสมาธิแบบมีสติได้รับการแสดงให้เห็นว่าช่วยปรับปรุงสมาธิและลดความสับสนทางจิตใจ แม้เพียง 10-15 นาทีต่อวันก็สามารถช่วยให้จิตใจสงบลง ทำให้ ความจำใช้งาน ของคุณทำงานได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพมากขึ้น
การติดตามความคืบหน้าของคุณ: เหตุใดการประเมินอย่างสม่ำเสมอจึงสำคัญ
คุณจะรู้ได้อย่างไรว่าความพยายามของคุณได้ผล? วิธีที่ดีที่สุดในการติดตามการปรับปรุงความรู้ความเข้าใจของคุณคือผ่านการประเมินอย่างสม่ำเสมอ การกำหนดข้อมูลพื้นฐานช่วยให้คุณเห็นว่าคะแนนของคุณเปลี่ยนแปลงไปอย่างไรเมื่อเวลาผ่านไปในขณะที่คุณใช้กลยุทธ์ใหม่ๆ
การตรวจสุขภาพสมอง เป็นประจำสามารถกระตุ้นให้คุณยึดติดกับพฤติกรรมสุขภาพที่ดี นอกจากนี้ยังให้ข้อเสนอแนะที่เป็นกลางเกี่ยวกับความคืบหน้าของคุณ มันเปลี่ยนเป้าหมายที่เป็นนามธรรมของ "การปรับปรุงความจำของฉัน" ให้เป็นเป้าหมายที่วัดผลได้และทำได้จริง

เสริมพลังจิตใจของคุณ: การเดินทางสู่ความจำใช้งานที่เพิ่มขึ้นของคุณเริ่มต้นขึ้นแล้ว
ความจำใช้งาน เป็นทักษะทางความรู้ความเข้าใจพื้นฐานที่กำหนดความสามารถในการเรียนรู้ ทำงาน และมีส่วนร่วมกับโลกของเรา แม้ว่าอาจเผชิญกับความท้าทายจากความเครียด ความชรา และไลฟ์สไตล์ แต่ก็ไม่ได้คงที่ ด้วยการทำความเข้าใจว่ามันคืออะไรและนำกลยุทธ์ที่ได้รับการสนับสนุนจากวิทยาศาสตร์มาใช้ คุณสามารถเสริมสร้างและสนับสนุนการทำงานของมันได้อย่างแข็งขัน
การเดินทางของคุณเริ่มต้นด้วยก้าวเดียว: การทำความเข้าใจสถานะของคุณในปัจจุบัน การได้รับความชัดเจนเกี่ยวกับจุดแข็งและจุดอ่อนทางความรู้ความเข้าใจของคุณเป็นการเสริมสร้างศักยภาพ มันให้แผนที่นำทางส่วนบุคคลสำหรับการเติบโตและการพัฒนาตนเอง
พร้อมที่จะค้นพบโปรไฟล์ความรู้ความเข้าใจของคุณแล้วหรือยัง? เริ่มการประเมินของคุณวันนี้ และก้าวแรกสู่จิตใจที่เฉียบคมและยืดหยุ่นยิ่งขึ้น
คำถามที่พบบ่อยเกี่ยวกับความจำใช้งานและการประเมินความรู้ความเข้าใจ
การประเมินความรู้ความเข้าใจคืออะไร และวัดอะไร?
การประเมินความรู้ความเข้าใจจะประเมินความสามารถทางจิตที่สำคัญของคุณ ครอบคลุมถึงความจำ (ระยะสั้นและใช้งาน) สมาธิ การทำงานของผู้บริหาร เช่น การวางแผน และความเร็วในการประมวลผล เป้าหมายคือการให้ภาพรวมที่ครอบคลุมของสุขภาพความรู้ความเข้าใจของคุณ
ฉันจะทดสอบความสามารถความจำใช้งานที่บ้านได้อย่างไร?
แม้ว่าคุณจะสามารถลองแบบฝึกหัดง่ายๆ เช่น การท่องรายการย้อนกลับได้ แต่เครื่องมือออนไลน์ที่มีโครงสร้างจะให้การวัดผลที่น่าเชื่อถือและเป็นกลางมากกว่า แพลตฟอร์มที่ออกแบบทางวิทยาศาสตร์สามารถให้คะแนนมาตรฐานและติดตามประสิทธิภาพของคุณเมื่อเวลาผ่านไป เพื่อให้ได้ข้อมูลพื้นฐานที่ถูกต้อง แม่นยำที่สุด ควร ทดสอบความสามารถทางความรู้ความเข้าใจของฉัน โดยใช้เครื่องมือที่ครอบคลุม
การทดสอบความรู้ความเข้าใจออนไลน์น่าเชื่อถือสำหรับความจำใช้งานหรือไม่?
ความน่าเชื่อถือของการทดสอบความรู้ความเข้าใจออนไลน์แตกต่างกันไปอย่างมาก แบบทดสอบออนไลน์ง่ายๆ อาจให้ความบันเทิงแต่ขาดการรับรองทางวิทยาศาสตร์ อย่างไรก็ตาม แพลตฟอร์มที่พัฒนาโดยนักประสาทจิตวิทยาและผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน AI ซึ่งอิงจากหลักการทดสอบที่เป็นที่ยอมรับ สามารถเชื่อถือได้อย่างมาก พวกเขานำเสนอวิธีที่สะดวกและแม่นยำในการประเมินการทำงานของการรับรู้ เช่น ความจำใช้งาน
จะเกิดอะไรขึ้นหากผลการทดสอบความจำใช้งานของฉันแสดงความท้าทาย?
การได้รับผลลัพธ์ที่บ่งชี้ถึงความท้าทายไม่ใช่การวินิจฉัยความผิดปกติ แต่ควรพิจารณาว่าเป็นข้อมูลที่มีค่า รายงานการประเมินที่ดีจะเน้นพื้นที่เหล่านี้และให้คำแนะนำที่นำไปใช้ได้จริงสำหรับการปรับปรุง เช่น การเปลี่ยนแปลงไลฟ์สไตล์และแบบฝึกหัดการฝึกสมองที่กล่าวถึงในบทความนี้ เป็นจุดเริ่มต้นสำหรับการเข้าถึงสุขภาพสมองของคุณอย่างเชิงรุก